James Webb Space Telescope
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the history of our Universe.

Key Facts
Featured Image
Click the image to enlarge, zoom, pan through the image.
NASA’s Webb Lifts Veil on Common but Mysterious Type of Exoplanet
Though they don’t orbit around our Sun, sub-Neptunes are the most common type of exoplanet, or planet outside our solar…
Read the Story
Latest News
Webb's latest news releases in reverse chronological order. Search and sort the news feed with the controls immediately below.

Though they don’t orbit around our Sun, sub-Neptunes are the most common type of exoplanet, or planet outside our solar system, that have been observed in our galaxy. These small, gassy planets are shrouded in mystery…and often, a lot of…

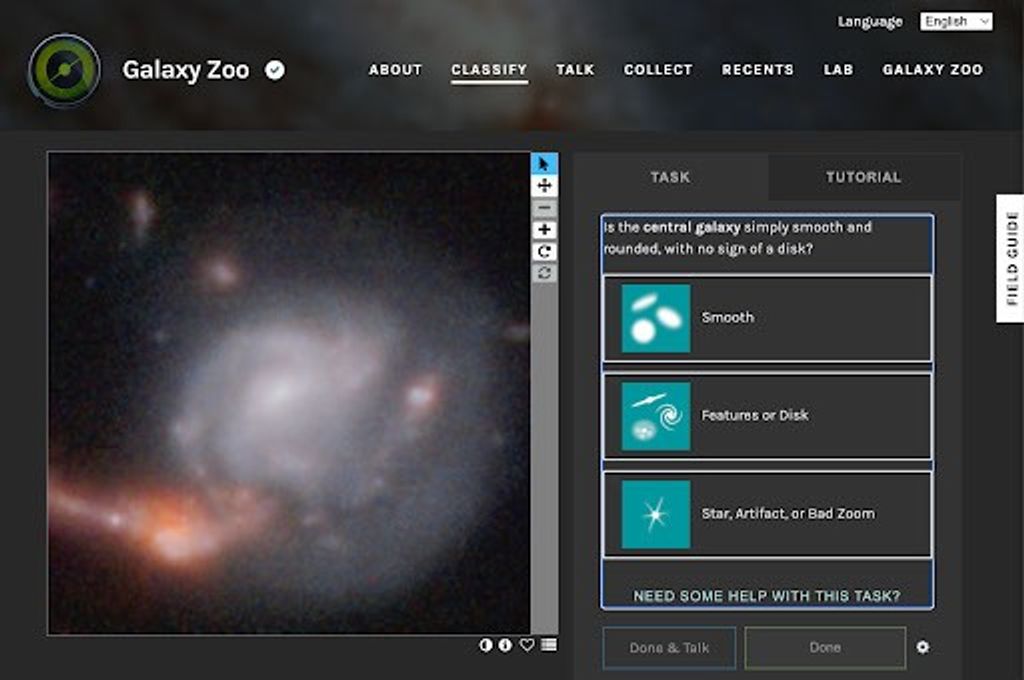
NASA needs your help identifying the shapes of thousands of galaxies in images taken by our James Webb Space Telescope with the Galaxy Zoo project. These classifications will help scientists answer questions about how the shapes of galaxies have changed…

How are we made of star stuff? Well, the important thing to understand about this question is that it’s not an analogy, it’s literally true. The elements in our bodies, the elements that make up our bones, the trees we…
Gas and dust ejected by a dying star at the heart of NGC 1514 came into complete focus thanks to mid-infrared data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Its rings, which are only detected in infrared light, now look like…
Webb's Blog
Webb's Blog offers an insider's point of view covering a variety of topics that include on going operations as well as exciting Webb science images/spectra that are not yet peer reviewed and therefore not released as NASA feature articles ( IE the above official Webb News Feed). Blog posts are often co-authored by scientists and engineers and offer unique insights. <strong>Search and sort the news feed with the controls immediately below.</strong>

This artist’s concept shows what exoplanet K2-18 b could look like based on science data. K2-18 b, an exoplanet 8.6 times as massive as Earth, orbits the cool dwarf star K2-18 in the habitable zone and lies 120 light-years from…

Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process. These results were reported as part of NASA’s role in the International Asteroid Warning Network. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope recently…

Trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) are icy bodies ranging in size from Pluto and Eris (dwarf planets with diameters of about 1,500 miles) down to tens of miles (Arrokoth) and even smaller. TNOs are on orbits comparable in size, or even much…
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is the largest and most powerful telescope ever launched to space. Its mirror is composed of 18 individual segments that have been aligned so accurately, that they effectively work as a single giant (21.6-foot, or…
Latest 2025 Images
The image below is a SLIDESHOW. Hover over the image to see the image title and controls. Click the image to go to a detail page with more info and the ability to download the image at various resolutions (click the downward arrow icon in lower right corner).
More Webb Images
What is Webb Observing?
See current, upcoming and recent past observations scientists are making with the Webb Space Telescope. View details about each observation's science focus areas, the instruments used and more.
View the Tool
The Webb Mission
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the history of our Universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own Solar System.
Learn More
Webb's Science Goals
The James Webb Space Telescope is a giant leap forward in our quest to understand the Universe and our origins. Webb is examining every phase of cosmic history: from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets to the evolution of our own solar system. Learn about the 4 main science themes for Webb.
Learn More
The Spacecraft
The Webb Space Telescope is the largest, most powerful and most complex telescope ever launched into space . It's design and development history stretches back before the Hubble Space Telescope was launched. Learn about the design, the major components and subsystems of Webb and see Webb in 3d in a 3d Solar System.
Learn More
The International Webb Team
Webb is for the world, and from the world. Thousands of skilled scientists, engineers and technicians from 14 countries (and more than 29 U.S. states, and Washington, D.C.) contributed to the design, build, test, integration, launch, commissioning and operations of Webb. It is a joint NASA/ESA/CSA mission. Assembly and testing of the mirror and instruments occurred at NASA Goddard (GSFC).
Learn More